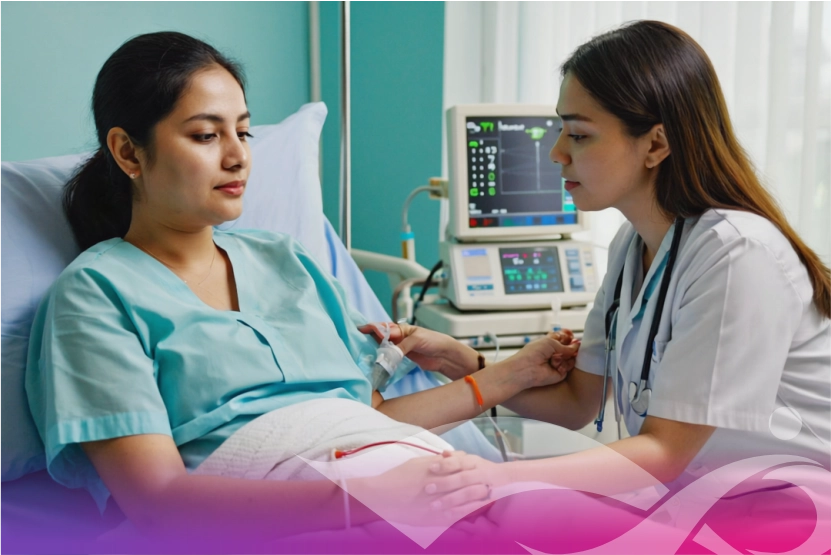
Cancer treatment is developing and new treatments once thought of as science fiction are starting to show up at an astonishing speed. One such novel treatment is CAR-T cell therapy, a form of immunotherapy in which a patient's own immune cells are genetically re-engineered to fight cancer. Many Indian patients ask: is this novel treatment available here, and for whom is it a reasonable choice? At IOCI, we are committed to provide our patients with global advancements in cancer therapy so as to ensure access to the most promising treatments. This advanced therapy represents a new frontier in Cancer diagnosis and treatment.
CAR-T cell therapy is what?
One very customised and sophisticated treatment is CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell) therapy. It entails several important phases:
- One type of immune cell called T-cells is collected from the patient's blood.
- Reprogramming: These T-cells are genetically changed in a specialised lab to produce surface chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). These CARs are designed to find and cling to specific proteins on the surfaces of cancer cells.
- The modified CAR-T cells are then multiplied in a lab to generate millions of these especially targeted cancer-fighting cells.
- Infusion: The enlarged CAR-T cells are pumped back into the patient's bloodstream just as in a blood transfusion. Once within the body, these "super-soldiers" T-cells hunt out and kill cancer cells displaying the target protein.
Because this treatment transforms the patient's own immune system into a highly targeted weapon against their cancer, it marks a major advance.
Does India offer CAR-T Therapy?
Indeed, CAR-T cell treatment is spreading over India more and more. Although this is a rather new and highly specialised treatment accessible worldwide, many top cancer centres in the country—including several connected with our network—now either offer or are ready to offer CAR-T therapy, especially for some haematological (blood) tumours.
Growing availability is being driven by developments in medical infrastructure, more oncology research funding, and international expert partnerships. Since CAR-T treatment is resource-intensive and highly specialised, facilities and knowledge are absolutely essential. Patients considering this treatment should consult experienced oncologists housed in facilities prepared to offer this advanced treatment.
Who Could Gain from CAR-T Therapy?
Currently, CAR-T cell therapy is most approved and most successful for some forms of blood cancers, especially:
- Relapsed or Refractory B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL): Often for paediatric and young adult patients whose ALL has not responded to other treatments or returned.
- Recurrent or Refractory Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): is for adults who have tried at least two other lines of treatment without success.
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): For adult patients whose MCL has relapsed or is refractory.
- For adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma,
- Particularly for patients with advanced or relapsed disease, CAR-T therapy is under ongoing clinical trials and has recently been approved for multiple myeloma.
As research develops, other blood malignancies and perhaps some solid tumours could find use for CAR-T treatment. Patients with malignant tumours who have not responded to conventional treatment nevertheless take the front stage.
Our multidisciplinary team at IOCI keeps current with the most recent global advancements, including those in CAR-T therapy. For patients grappling with lymphoma types and treatment, especially those with challenging prognoses, we evaluate all available cutting-edge options to determine the most appropriate and effective course of action. We provide comprehensive counseling to discuss whether CAR-T therapy or other advanced treatments are suitable, ensuring that each patient receives the best possible care tailored to their unique condition, and that they understand causes of cancer in young adults.
Consult us at any of our locations—across IOCI Noida, Greater Noida, Mumbai, Indore, Aurangabad, Agartala, Saharanpur, Kanpur and Jodhpur.